ECONOMIC REVIEW
Based on the observed trends, especially the vaccination efforts, it is projected that economic recovery will occur gradually in line with vaccination rates and the occurrence of herd immunity. In general, global economies are expected to continue to recover positively and reach 2019 GDP levels between 2021 and 2022, based on projections by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank. For example, China as the country that experienced the earliest COVID-19 pandemic experienced a significant economic recovery and exceeded the GDP value in 2019. Meanwhile, other countries such as America and India are expected to experience recovery, exceeding the 2019 GDP value in 2021-2022. European countries and Japan are expected to recover in 2022. A comparison can be seen below. In addition to GDP, other indicators such as the Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Indeks (PMI), retail and creation mobility, passenger vehicle sales, and the level of retail sales also showed a positive rate of recovery.
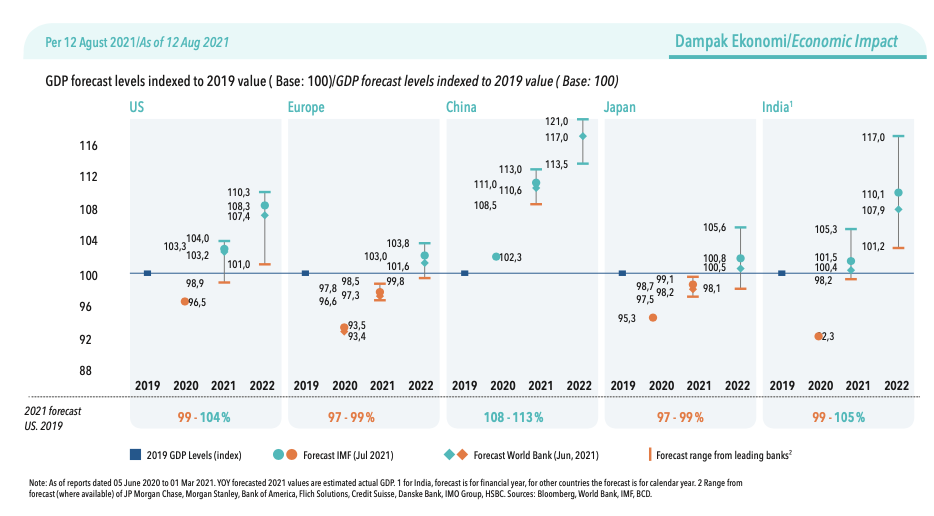
Nevertheless, there is still uncertainty concerning the global economic recovery. In general, global economic recovery is influenced by several factors related to COVID-19 infection: (1) increased infections of the delta variant, (2) vaccination rates, (3) the possibility of the emergence of new, more dangerous variants. The spread of the delta variant has been observed in many countries in the last few months. In some countries, we can see an increase in the spread of the delta variant after the easing of social restrictions. The rise in infections has also led to a new wave of infections in countries that previously showed a good recovery. So far the vaccines have been shown to help
